Optimizing Payment Success Across all Subscription Billing Events
Introduction
For subscription businesses, revenue depends on successfully processing recurring payments. There are three critical billing events when payments could be approved or declined: the initial signup, recurring subscription billing, and retries after a payment is declined. In other words, there are three
times when revenue can be generated or lost.
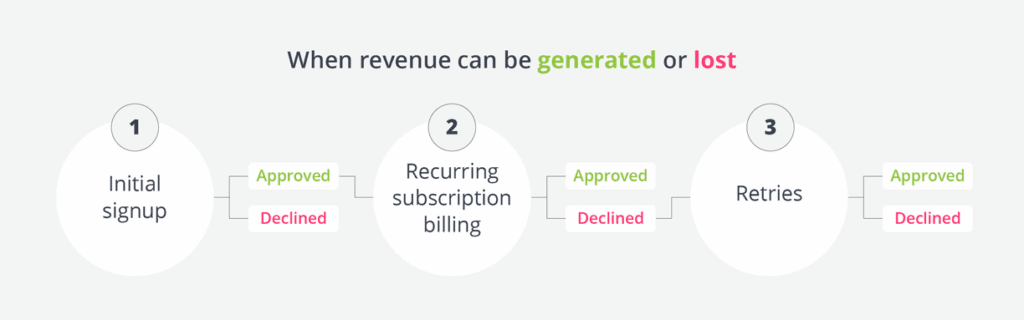
Approval outcomes at each stage of the billing cycle have a direct impact on revenue, retention, and long-term business growth. Payment success and customer retention are directly connected — in fact up to 50% of customer churn is caused by involuntary churn, often the result of failed payments. An
approved transaction creates a seamless customer experience, but when a payment fails — especially without a clear explanation or timely resolution — trust can be eroded. Many customers won’t return after a failed payment, particularly if it happens at the beginning of their journey or the situation feels
like it would be a hassle to resolve. On the other hand, reliable payment processing builds confidence and reduces friction throughout the customer lifecycle. The better your payment performance, the less likely customers are to leave.
This eBook explores the importance of optimizing payment success across all three billing events and offers strategies and suggestions to help subscription businesses improve payment success, increase revenue, and prevent churn.
Understanding Card Payment Authorization Requests
Optimizing payment approvals isn’t just about fixing failed transactions after the fact. It starts with understanding how credit card authorization requests (the process where a business asks a card issuing bank for approval to charge a customer’s credit card) differ depending on the billing event.
Credit card transactions fall into two categories under card network rules:
• Customer-Initiated Transactions (CIT): Triggered by the customer, typically at signup.
• Merchant-Initiated Transactions (MIT): Triggered by the business using stored credentials, such as for recurring billing or retries after a decline.
These categories affect how banks assess risk and decide whether to approve or decline a transaction. Card issuers evaluate the risk profile of each of these billing events differently, which requires merchants to tailor their payments strategy for each event.

Initial Signup – Customer-Initiated Transaction (CIT)
What happens
During the initial signup, the subscriber enters their credit card details in the shopping cart. This is classified as a Customer-Initiated Transaction (CIT) under the frameworks of the card networks.
Why it matters
This is the first and often most critical touchpoint in the customer lifecycle. A failed authorization here
often leads to shopping cart abandonment, resulting in immediate loss of revenue and the potential
loss of the customer entirely.
Reasons why cards may be declined at signup

Ways to increase approval rates at signup
• Real-Time Card Validation: Use tools like Luhn check, Address Verification System (AVS), and Card Verification Value (CVV) validation before authorization. These checks help catch errors or mismatches before a transaction is submitted to the bank, reducing avoidable declines.
• Network Tokenization: Implement Visa and Mastercard network tokens to reduce declines due to fraud concerns or card reissuance. Tokenization is a payment security technology that replaces a customer’s actual credit card number with a unique, non-sensitive token. This token is used for storing and processing payments instead of the real card number. Tokenization also helps maintain continuity if a card is replaced after loss or theft, keeping the payment method up to date without requiring customer input.
• 3D Secure 2.0 (for high-risk regions/products): Use 3DS2 as an extra authentication layer to reduce false declines. This upgraded authentication protocol makes online credit and debit card transactions more secure and improves the checkout experience for customers, although the
extra steps can cause more cart abandonment.
• Clear Merchant Category Code (MCC): MCCs help banks understand what your business sells, and misaligned codes can cause unnecessary fraud concerns or declines. Use the right MCC for your business to ensure it aligns with card network expectations for your product type.
• Retry logic for soft declines: Soft declines are temporary issues—like a momentary system outage or insufficient funds—that might succeed if retried shortly after using intelligent retry strategies.
Recurring Subscription Billing – Merchant-Initiated Transaction (MIT)
What happens
On a regular cycle (e.g., monthly, quarterly, or annually) the merchant submits a transaction to the processor using previously stored credentials. This is a Merchant-Initiated Transaction (MIT) under stored credential rules. Unlike signups, these transactions occur without the customer being present or
actively participating at the time of billing.
Why it matters
Recurring billing is the core of subscription revenue. When a recurring charge fails, the customer may lose access to the service—often without realizing the issue or how to fix it. If not addressed promptly, this can lead to lost customers and revenue.
Reasons why cards may be declined on renewal cycles

Ways to increase approval rates at signup
• Card Updater Services: Use Visa Account Updater (VAU) and Mastercard Automatic Billing Updater (ABU) to keep credentials current. These services automatically update expired or replaced cards, reducing declines caused by outdated information.
• Use MIT flag properly: Ensure transactions are flagged as MIT and properly linked to the original CIT. This signals to the issuer that the customer previously approved the transaction, which helps reduce fraud concerns and increase approval likelihood.
• Ensure usage of proper Merchant Category Code (MCC): Card issuers use MCCs to evaluate the risk and legitimacy of a transaction. Make sure your MCC aligns with your offering and your issuer’s expectations for your type of business. An incorrect or mismatched MCC can cause confusion or make your billing look suspicious, especially for subscription services.
• Consistent Billing Descriptor: Use a recognizable descriptor to prevent customer disputes or chargebacks. The billing descriptor is what appears on a customer’s credit card statement. If it’s unclear or unfamiliar, customers may contact their bank to dispute the charge, leading to a decline
or chargeback.
Retry After Decline – Revenue Recovery Phase
What happens
When a transaction fails during recurring billing, you can retry the card after a short delay, ideally applying strategies optimized to deliver an approval result from the card issuer. This retry is still considered a Merchant-Initiated Transaction, but it now falls into the revenue recovery or optimization phase, where the focus is on salvaging lost revenue.
Why it matters
This is your last chance to recover revenue that would otherwise be lost. However, poorly managed retries can do more harm than good, potentially annoying the customer and increasing churn.
Poorly managed retries can do more harm than good, potentially annoying customers and increasing churn.
Reasons why cards may be declined on renewal cycles

Ways to increase approval rates at signup
• Intelligent Retries: Each issuing bank maintains its own payment authorization rules, and each declined payment may have one of hundreds of decline codes. A one-size-fits-all retry approach won’t work. The most effective recovery systems tailor retries based on decline reason, issuer
behavior, and optimal timing.
• Dynamic Routing: Use alternate acquirers or payment gateways with higher approval rates in certain geographies or card brands, if possible. Routing transactions through different processors can help when one provider is underperforming with specific banks or card networks.
• Effective Customer Communications: Implement customer notifications via email, SMS, or app alerts with clear instructions on how to update payment details. This is especially important when a retry won’t work without action—such as when a card has expired or been closed.
• AI-Powered Recovery: Use a sophisticated failed payment recovery solution designed to optimize recovery and reduce involuntary churn. AI can detect patterns and adjust strategies in real-time, significantly improving recovery rates and reducing involuntary churn.
Using a sophisticated AI-powered failed payment recovery solution will increase revenue and reduce involuntary churn.
The Ideal Failed Payment Recovery Solution

To achieve longer customer retention and higher LTV values, companies need a payment recovery experience that’s either works silently in the background or delivers a positive, low-friction experience that motivates the customer to successfully solve their payment issue.
This is exactly what you get with the combined power of FlexPay’s Invisible Recovery™ + Engaged Recovery™ solutions.
Invisible Recovery uses AI to automatically retry failed transactions with the right strategy, timing, and routing – without any customer involvement. This method can recover as high as 70% of failed payments while maximizing customer retention following recovery.
When Invisible Recovery alone isn’t enough, Engaged Recovery steps in. This strategy uses intelligent customer outreach—via email, SMS, or in-app prompts—to guide the customer through resolving their payment issue. Engaged Recovery can add an additional 30% to your recovery rates.
While individual company results will vary, only FlexPay offers this level of performance to help subscription companies of all sizes recover more failed payments and reduce their rate of involuntary churn.
Conclusion
Every payment authorization is more than just a transaction—it’s a key moment in the customer experience. When payments succeed, you generate revenue and strengthen retention. When they fail, you risk customer frustration, lost trust, and eventual churn. That’s why optimizing payment performance at every subscription billing event is so important.
Subscription businesses that take a strategic, preventative approach at each of these key moments can:
• Minimize avoidable declines from the start
• Recover more revenue when payments do fail
• Strengthen customer relationships and boost long-term value
With the right tools and strategy, improving payment performance becomes a manageable process with measurable returns. Whether you’re just starting to optimize or looking to fine-tune your existing payment strategy, purposefully targeting each billing event will lead to stronger financial results and improved customer relationships month after month.

